GO TO MY PRIVATE PAGE
GO TO BOTTOM
Go to Bioinformatics Tools
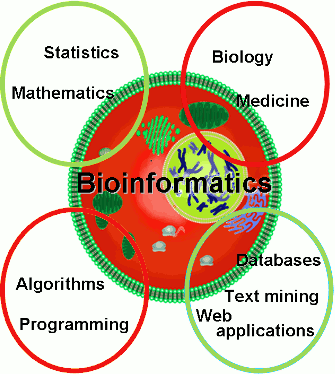
BIOINFORMATICS
Bioinformatics is the application of information technology to the field of molecular biology. The term bioinformatics
was coined by Paulien Hogeweg in 1979
for the study of informatic processes in biotic systems. Bioinformatics now entails the creation and advancement of databases, algorithms, computational
and statistical techniques, and theory to solve formal and practical problems arising from the management and analysis of biological data. Over the past
few decades rapid developments in genomic and other molecular research technologies and developments in information technologies have combined to produce a
tremendous amount of information related to molecular biology. It is the name given to these mathematical and computing approaches used to glean understanding
of biological processes. Common activities in bioinformatics include mapping and analyzing DNA and protein sequences, aligning different DNA and protein
sequences to compare them and creating and viewing 3-D models of protein structures.
The primary goal of bioinformatics is to increase our understanding of biological processes. What sets it apart from other approaches, however, is its focus
on developing and applying computationally intensive techniques (e.g., pattern recognition, data mining, machine learning algorithms, and visualization) to
achieve this goal. Major research efforts in the field include sequence alignment, gene finding, genome assembly, protein structure alignment, protein
structure prediction, prediction of gene expression and protein-protein interactions, genome-wide association studies and the modeling of evolution.
Bioinformatics was applied in the creation and maintenance of a database to store biological information at the beginning of the "genomic revolution", such a
s nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Development of this type of database involved not only design issues but the development of complex interfaces whereby
researchers could both access existing data as well as submit new or revised data.
In order to study how normal cellular activities are altered in different disease states, the biological data must be combined to form a comprehensive picture
of these activities. Therefore, the field of bioinformatics has evolved such that the most pressing task now involves the analysis and interpretation of
various types of data, including nucleotide and amino acid sequences, protein domains, and protein structures. The actual process of analyzing and interpreting
data is referred to as computational biology. Important sub-disciplines within bioinformatics and computational biology include:
a) the development and implementation of tools that enable efficient access to, and use and management of, various types of information.
b) the development of new algorithms (mathematical formulas) and statistics with which to assess relationships among members of large data sets, such as
methods to locate a gene within a sequence, predict protein structure and/or function, and cluster protein sequences into families of related sequences.
BIOINFORMATICS TOOLS

SUBCELLULAR TARGETING PREDICTION
EXPLANATION OF BIOINFORMATICS TOOLS
HTML (HYPERTEXT MARK UP LANGUAGE)
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, is the predominant markup language for web pages. It provides a means to create structured documents by
providing different structural elements for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists etc as well as for links, quotes, and other items. It allows images and objects
to be placed and can be used to create interactive forms. It is written in the form of HTML elements consisting of "tags" surrounded by angle brackets
within the web page content.
HTML is the code behind our webpage and is a series of tags that tells the browser where to display what. It is really a series of simple commands that
we give to the browser For example, if we want our text to show in a bold type, the command is to be bold
text .
HTML works in a very simple and very logical format. It reads top to bottom, left to right. HTML is written with TEXT. What we use to set certain sections apart
as bigger text, smaller text, bold text, underlined text, is a series of tags.
Tags are like commands.
All tags that are opened must correspondingly be closed, just as if we are writing a quoted statement with those "inverted commas". A tag is closed
this way .
Different tags call different functions.
TOOLS RELATED TO HTML
- HTML CODE TUTORIAL
Here we can find the free html tutorial that helps us to create a web page. The html tutorial helps us to write codes in html.
- HTML COLOR CODES
Here we can get the hexadiecmal codes for different colors that can make our web page more attractive.
- HTML Books
On this website you can some books on HTML.
- FREE HTML TEMPLATES
If you want to make your web page more interactive you can use templates. On this page you can download some freely available templates.
- DOMAIN NAMES
On this page you can find more about domain names and how to register your website.
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a set of computer programs that controls the creation, maintenance, and the use of the database of an organization
and its end users. It allows organizations to place control of organization-wide database development in the hands of database administrators (DBAs) and
other specialists. DBMSes may use any of a variety of database models, such as the network model or relational model. In large systems, a DBMS allows users
and other software to store and retrieve data in a structured way. It helps to specify the logical organization for a database and access and use the
information within a database. It provides facilities for controlling data access, enforcing data integrity, managing concurrency controlled, restoring
database.
COMPUTATIONAL STEPS
In Bioinformatics there is great involvement of computer applications and information technology. different computer languages are used for creating softwares,
tools, programs etc. Mostly we use Visual basics, C++ and Perl but some bioinformaticians also use fortan and other higher languages for scripting.
RAW DATA
Here raw data refers to the sequences of genes and proteins that we atke from wet lab experiments or we can say that product of biotechnological experiments. We
use raw data for further processing as in case of data mining, in order to remove redundancy and to keep only relevant sequences. This refined data is then stored
in databases, so that it could be avalable to researchers world wide.
Sequence Allignments
Sequence allignment and structure prediction are the major elements of Bioinformatics that are used often in the scientific study.
The programs that are used to carry out sequence allignments are BLAST
FASTA. These two programs are use for the allignment of paired sequences but if we want to
do sequence allignment of multiple sequences then we can use CLUSTAL W.
Secondary Structure Prediction
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, is the predominant markup language for web pages. It provides a means to create structured documents by providing different structural elements for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists etc as well as for links, quotes, and other items. It allows images and objects to be placed and can be used to create interactive forms. It is written in the form of HTML elements consisting of "tags" surrounded by angle brackets within the web page content.
HTML is the code behind our webpage and is a series of tags
HTML works in a very simple and very logical format. It reads top to bottom, left to right. HTML is written with TEXT. What we use to set certain sections apart as bigger text, smaller text, bold text, underlined text, is a series of tags. Tags are like commands.
All tags that are opened must correspondingly be closed, just as if we are writing a quoted statement with those "inverted commas". A tag is closed this way . Different tags call different functions.
Here we can find the free html tutorial that helps us to create a web page. The html tutorial helps us to write codes in html.
Here we can get the hexadiecmal codes for different colors that can make our web page more attractive.
On this website you can some books on HTML.
If you want to make your web page more interactive you can use templates. On this page you can download some freely available templates.
On this page you can find more about domain names and how to register your website.
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a set of computer programs that controls the creation, maintenance, and the use of the database of an organization and its end users. It allows organizations to place control of organization-wide database development in the hands of database administrators (DBAs) and other specialists. DBMSes may use any of a variety of database models, such as the network model or relational model. In large systems, a DBMS allows users and other software to store and retrieve data in a structured way. It helps to specify the logical organization for a database and access and use the information within a database. It provides facilities for controlling data access, enforcing data integrity, managing concurrency controlled, restoring database.
In Bioinformatics there is great involvement of computer applications and information technology. different computer languages are used for creating softwares, tools, programs etc. Mostly we use Visual basics, C++ and Perl but some bioinformaticians also use fortan and other higher languages for scripting.
Here raw data refers to the sequences of genes and proteins that we atke from wet lab experiments or we can say that product of biotechnological experiments. We use raw data for further processing as in case of data mining, in order to remove redundancy and to keep only relevant sequences. This refined data is then stored in databases, so that it could be avalable to researchers world wide.
Sequence allignment and structure prediction are the major elements of Bioinformatics that are used often in the scientific study. The programs that are used to carry out sequence allignments are BLAST FASTA. These two programs are use for the allignment of paired sequences but if we want to do sequence allignment of multiple sequences then we can use CLUSTAL W.
GO TO TOP